목차
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter의 요청 및 응답 처리 전체 구조
https://kimyongjun0129.tistory.com/185
[Spring] Spring MVC, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter의 요청 및 응답 처리 과정
목차RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 구조용어 정리전체 흐름 요약 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 구조 용어 정리DispatcherServlet : Spring MVC의 핵심 프론트 컨트롤러클라이언트의 모든 요청을 가로채고, 적적할 컨트롤
kimyongjun0129.tistory.com
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 구조

- 요청 시, `Argument Resolver`가 HttpMessageConverter 를 사용합니다.
- 응답 시, `Return Value Handler`가 HttpMessageConverter 를 사용합니다.
HttpMessageConverter
정의
HTTP 요청의 Body를 Java 객체로 변환하는 역직렬화, Java 객체를 HTTP 응답의 Body로 변환하는 직렬화를 수행합니다.
- 주로 컨트롤러 메서드의 파라미터에 `@RequestBody`가 붙은 경우 요청 본문을 역직렬화하기 위해 `HttpMessageConverter`를 호출합니다.
- 반환값에 `@ResponseBody` 또는 클래스에 `@RestController`가 붙은 경우 응답 본문으로 직렬화하기 위해 `HttpMessageConverter`를 호출합니다.
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 구현체가 호출합니다.
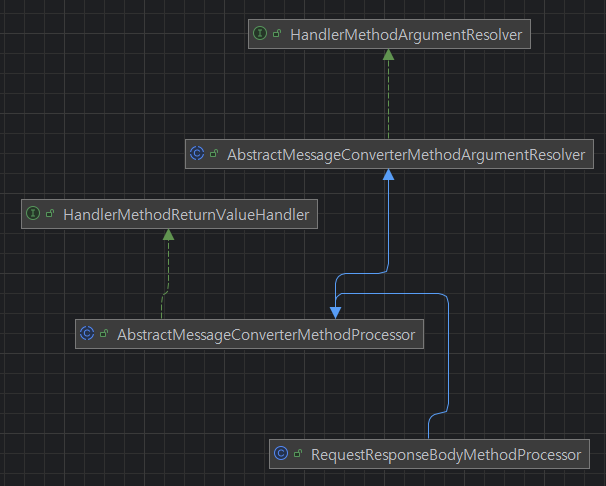
- `@RequestBody`와 `@ResponseBody` 처리는 Spring MVC에서 각각 다음 방식으로 이루어집니다
- `RequestBody` 처리
- 클라이언트의 JSON 요청을 Java 객체로 변환하기 위해 사용합니다.
- Spring MVC는 이 작업을 위해 `HandlerMethodArgumentResolver` 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스인 `RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor`를 사용합니다.
- `ResponseBody` 처리
- Java 객체를 JSON 등의 형태로 직렬화(serialize)하여 클라이언트에게 반환하기 위해 사용합니다.
- Spring MVC는 이 작업을 위해 `HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler` 인터페이스를 구현한 `RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor`를 사용합니다.
- `RequestBody` 처리
- 따라서 이 `RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor` 구현체는 `HandlerMethodArgumentResolver`와 `HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler`를 둘 다 구현해야 합니다.
✨ `RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor` 구현체는 ArgumentResolver 구현체이면서도 ReturnValueHandler 구현체입니다.
HttpMessageConverter 종류
| 클래스 이름 | 설명 | Content-Type |
| `MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter` | Jackson을 이용해 JSON ↔ Java 객체 변환 | `application/json` |
| `JsonbHttpMessageConverter` | JSON-B API(JSR 367)를 이용한 JSON 처리 | `application/json` |
| `StringHttpMessageConverter` | 문자열을 그대로 처리 | `text/plain`, 기타 |
| `FormHttpMessageConverter` | HTML form 데이터 처리 (`application/x-www-form-urlencoded`) | `application/x-www-form-urlencoded` |
| `ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter` | 바이너리 데이터 처리 | `application/octet-stream`, 이미지 등 |
| `ResourceHttpMessageConverter` | `Resource` (파일, 클래스패스 리소스 등) 전송 | 파일 다운로드 등 |
| `SourceHttpMessageConverter` | XML 처리 (JAXP의 `Source` 사용) | `application/xml`, `text/xml` 등 |
| `Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter` | JAXB를 이용한 XML ↔ Java 객체 변환 | `application/xml`, `text/xml` |
| `ProtobufHttpMessageConverter` | Protocol Buffers 메시지 처리 | `application/x-protobuf` |
- Spring Boot를 사용하면 기본적으로 등록되는 컨버터들이 있습니다.
- JSON 처리 : `MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter` (기본 JSON 라이브러리)
- 문자열 : `StringHttpMessageConverter`
- 폼 데이터 : `FormHttpMessageConverter`
- 바이너리 : `ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter`
- XML (선택적으로) : `Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter` 등
- `WebMvcConfigurer`를 구현해 커스텀 컨버터를 추가로 등록할 수 있습니다.
내부 구조

- 각 Converter 클래스들은 이 인터페이스를 간접적으로 구현한 형태입니다.
- 이 인터페이스를 구현하여, 커스텀하게 Converter를 만들 수 있습니다. (확장)
- 메서드
- `canRead()` :
이 컨버터가 주어진 클래스 타입과 미디어 타입(`Content-Type`)을 가진 HTTP 요청을 읽을 수 있는지 여부를 판단합니다. - `canWrite()` :
이 컨버터가 주어진 클래스 타입과 미디어 타입을 사용해 Java 객체를 HTTP 응답으로 변환(직렬화) 할 수 있는지를 판단합니다. - `getSupportedMediaTypes();` :
이 컨버터가 지원하는 Content-Type 목록을 반환합니다. (예: application/json, application/xml, text/plain 등) - `getSupportedMediaTypes(Class<?> clazz);` :
특정 클래스에 대해 지원 가능한 미디어 타입을 반환합니다. 기본 구현은 `canRead()` 또는 `canWrite()`가 가능한 경우에만 `getSupportedMediaTypes()` 결과를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 빈 리스트를 반환합니다. - `read()` :
HTTP 요청 바디 (`HttpInputMessage)를 읽어서 Java 객체로 역질렬화(Deserialization) 합니다. - `write()` :
Java 객체 `t`를 HTTP 응답 바디 (`HttpOutput`Message`)에 직렬화(Serialization)하여 씁니다.
- `canRead()` :
실제 동작 순서 (역직렬화)
1. HttpMessageConverter 선택
- `RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor` 구현체가 등록된 `HttpMessageConverter` 리스트를
우선순위대로 순회합니다.
@Override
public Object resolveArgument(...) {
...
return readWithMessageConverters(request, methodParam, paramType);
}
2. 각 `HttpMessageConverter`들은 `canRead()` 메서드로 Class, MediaType 지원여부를 체크합니다.
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);- 만족하면 `true`를 반환합니다. `true`를 반환한 Converter가 선택됩니다.
(예: `MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter`)
2. `read()` 메서드로 HttpMessage를 읽습니다.
T read(
Class<? extends T> clazz,
HttpInputMessage inputMessage
) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;- `clazz` : 최종적으로 생성해야 할 객체 타입 (예: `user.class`)
- `inputMessage` : HTTP 요청 본문을 읽을 수 있게 추상화한 객체 (`InputStream` 제공)
- 이 정보를 통해, 구현체에서 `JSON → Java 객체`로 변환합니다.
✨ 직렬화 과정도 역직렬화와 비슷합니다.
✨ Spring은 다양한 HttpMessageConverter를 제공하고 있고 우선순위가 있습니다. 대상 Class와 MediaType을 체크해서 어떤 Converter를 사용할지 결정합니다.
순서 : `byte[]` -> `String` -> `Object`,`HashMap`
대표적인 HttpMessageConverter
1. `ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter`
- `byte[]` Data를 처리한다.
- 대상 : `byte[]`
- MediaType : `*/*`
- 반환 : `application/octet-stream`
@Slf4j
@RestController // @Controller + @ResponseBody
public class MessageConverterController {
// 요청 헤더 -> content-type: */*
@PostMapping("/byte-array")
// byte[] -> produces = "application/octext-stream"
public byte[] byteArray(@RequestBody byte[] data) {
log.info("byte-array logic");
return data; // response
}
}
2. `StringHttpMessageConverter`
- `String` Data를 처리합니다.
- 대상 : `String`
- MediaType : `*/*`
- 반환 : `text/plain`
// 요청 헤더 -> content-type: text/plain
@PostMapping("/string")
// String -> produces = "text/plain"
public String string(@RequestBody String data) {
log.info("string logic");
return data;
}
3. `MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter`
- `JSON` Data를 처리합니다.
- 대상 : `Object`, `HashMap`
- MediaType : `application/json`
- 반환 : `application/json`
// 요청 헤더 content-type: application/json
@PostMapping("/json")
// Data -> produces = "application/json"
public Data json(@RequestBody Data data) {
log.info("json logic");
return data;
}
4. 기타
- 이외에도 기본적으로 제공되는 다양한 MessageConverter가 존재한다.
- 대부분의 경우 위 세가지로 해결이 된다.


